Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) is a high-performance composite material that combines the exceptional strength and stiffness of carbon fibers with the lightweight and moldable properties of polymer resins. This unique combination results in a remarkably strong, lightweight, and versatile material with a wide range of applications across various industries.

Comparison of Load-Bearing Capacity, Heat Resistance, Impact Resistance, and Fatigue Strength between CFRP and Other Materials
| Property | CFRP | Steel | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load-bearing capacity | Very high, superior to steel in specific strength (strength-to-weight ratio). | Very high, especially for high-strength steel. | Relatively high, but lower than steel. |
| Heat resistance | Excellent, can withstand temperatures exceeding 200°C (depending on the resin) and retains high strength. | Good, can withstand high temperatures. | Good, but inferior to steel at high temperatures. |
| Impact resistance | Good, can absorb impact energy, but can be brittle under certain conditions. | Relatively good, but may be permanently deformed after a strong impact. | Good, but inferior to GFRP. |
| Fatigue strength | Excellent, superior to steel and aluminum, ideal for applications with repeated loading. | Good, but may experience fatigue if subjected to varying loads over a long period. | Good, but inferior to CFRP. |
| Specific gravity | Extremely light, about 1/5 to 1/7 the weight of steel. | Heavy. | Lighter than steel but heavier than CFRP. |
Deep Dive into CFRP vs. GFRP
Expanding on the Comparative Table
Let’s delve deeper into the comparison between CFRP and GFRP, focusing on some key differences and similarities:
| Feature | CFRP | GFRP |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Higher due to the complex manufacturing process of carbon fibers. | Lower compared to CFRP but higher than traditional materials. |
| Electrical Conductivity | Can be conductive or non-conductive depending on the resin system. | Generally non-conductive. |
| Fatigue Life | Excellent, making it suitable for applications with cyclic loading. | Good, but slightly lower than CFRP. |
| Environmental Impact | Manufacturing process can be energy-intensive, but the materials themselves are non-corrosive. | Manufacturing process is less energy-intensive, but the material is susceptible to UV degradation if not properly protected. |
| Specific Applications | Aerospace, Formula 1 racing, high-performance sports equipment, electronic devices. | Construction, marine, automotive, chemical processing. |
Additional Considerations
- Manufacturing Process: While both materials are produced through a similar process, the manufacturing of carbon fibers is more complex and energy-intensive, contributing to the higher cost of CFRP.
- Resin Systems: The choice of resin system significantly impacts the properties of both CFRP and GFRP. For example, epoxy resins are commonly used in CFRP due to their high performance, while polyester resins are more commonly used in GFRP for their lower cost.
- Design Flexibility: Both materials offer excellent design flexibility, but CFRP’s higher stiffness and strength allow for more complex and demanding designs.
Key Takeaways
- CFRP is the premium choice for applications demanding maximum strength, stiffness, and lightweight properties, such as aerospace and high-performance racing. Its superior mechanical properties and fatigue life make it ideal for critical components.
- GFRP offers a good balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. It is widely used in construction, marine, and automotive applications.
Comparative Applications
| Application | CFRP | GFRP |
|---|---|---|
| Aircraft components | Wings, fuselage, control surfaces | Interior panels, non-structural components |
| Automotive | Chassis, body panels, racing car components | Body panels, corrosion-resistant components |
| Marine | High-performance boat hulls, masts | Boat hulls, decks, marine equipment |
| Construction | Structural reinforcement, bridge components | Roofing, cladding, corrosion-resistant pipes |
Conclusion
Both CFRP and GFRP offer unique advantages and are well-suited for a wide range of applications. The choice between the two materials depends on factors such as performance requirements, cost constraints, and environmental considerations. By carefully evaluating the specific needs of an application, engineers and designers can select the optimal material to achieve the desired outcomes.
Detailed Explanation:
- Load-bearing capacity: CFRP offers superior specific strength compared to steel. This translates to lighter structures with exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum strength with minimal weight.
- Heat resistance: The heat resistance of CFRP depends on the type of resin used. However, CFRP generally offers excellent heat resistance compared to other materials, making it suitable for high-temperature environments.
- Impact resistance: CFRP can absorb impact energy, but its impact resistance can vary depending on the fiber orientation and resin system. It may be more brittle than steel or aluminum under certain impact conditions.
- Fatigue strength: CFRP boasts exceptional fatigue strength, making it ideal for applications experiencing repeated loads without significant performance degradation.
- Specific gravity: CFRP’s incredibly low weight offers significant advantages in reducing overall weight, leading to lower transportation and fuel consumption costs.
Additional Images:
- A comparison chart showcasing the tensile strength, compressive strength, and modulus of elasticity of CFRP, steel, and aluminum.
- Images of CFRP products used in various applications (e.g., aircraft parts, racing car components, high-performance sporting goods).
- A micrograph of the carbon fibers and resin matrix in a CFRP composite.
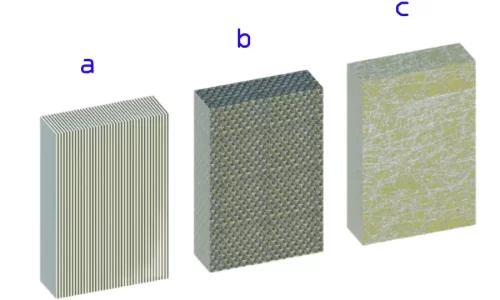
The Structure of CFRP
CFRP composites consist of two primary components:
- Carbon Fibers: These high-strength, high-stiffness fibers form the backbone of the composite, providing exceptional strength and stiffness to the material.
- Polymer Resin: The resin matrix binds the carbon fibers together, transfers load between the fibers, and protects them from environmental factors.
Advantages of CFRP
- Unmatched Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Offers exceptional strength and stiffness while being incredibly lightweight.
- Superior Corrosion Resistance: Highly resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for harsh environments.
- Exceptional Design Flexibility: Can be tailored into various shapes and sizes for diverse applications.
- Outstanding Durability: Offers a long lifespan with minimal maintenance requirements.
- Low Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Excellent insulator for thermal and electrical applications.
Applications of CFRP
CFRP’s unique properties have led to its extensive use in various industries:
- Aerospace: Aircraft wings, fuselage components, spacecraft structures.
- Automotive: High-performance vehicles, racing car parts, lightweight chassis components.
- Sports and Leisure: High-end bicycles, tennis rackets, golf clubs, sporting equipment.
- Marine: High-performance boat hulls, masts, spars.
- Industrial: Machinery components, pressure vessels, high-pressure pipes.
- Construction: Reinforcement for bridges and buildings, seismic retrofitting materials.
- Medical: Prosthetic limbs, medical equipment.
Why Choose CFRP?
CFRP offers a cutting-edge solution for numerous industries due to its exceptional properties. Choosing CFRP provides several key benefits:
- Reduced Weight: Significantly lowers transportation costs and improves fuel efficiency in vehicles and aircraft.
- Enhanced Strength and Durability: Offers superior strength-to-weight ratio, leading to longer lifespans and reduced maintenance
At 76Plastic, we understand that every customer has unique requirements. That’s why we offer a wide range of customization options for our 1 CFRP products. Whether you need a specific size, shape, or surface finish, our team can work with you to create a custom solution that meets your exact needs. Our dedicated team of engineers and technicians is always available to provide expert advice and support throughout the entire process, from design to delivery.




No comments.
You can be the first one to leave a comment.