Definition: Epoxy resin is a synthetic polymer formed through a chemical reaction between epoxy and a curing agent.
Structure: Epoxy resin has a unique molecular structure, creating very strong chemical bonds when combined with a curing agent.
Properties: Epoxy resin possesses numerous superior properties such as high strength, heat resistance, water resistance, chemical resistance, electrical insulation, and excellent adhesion.
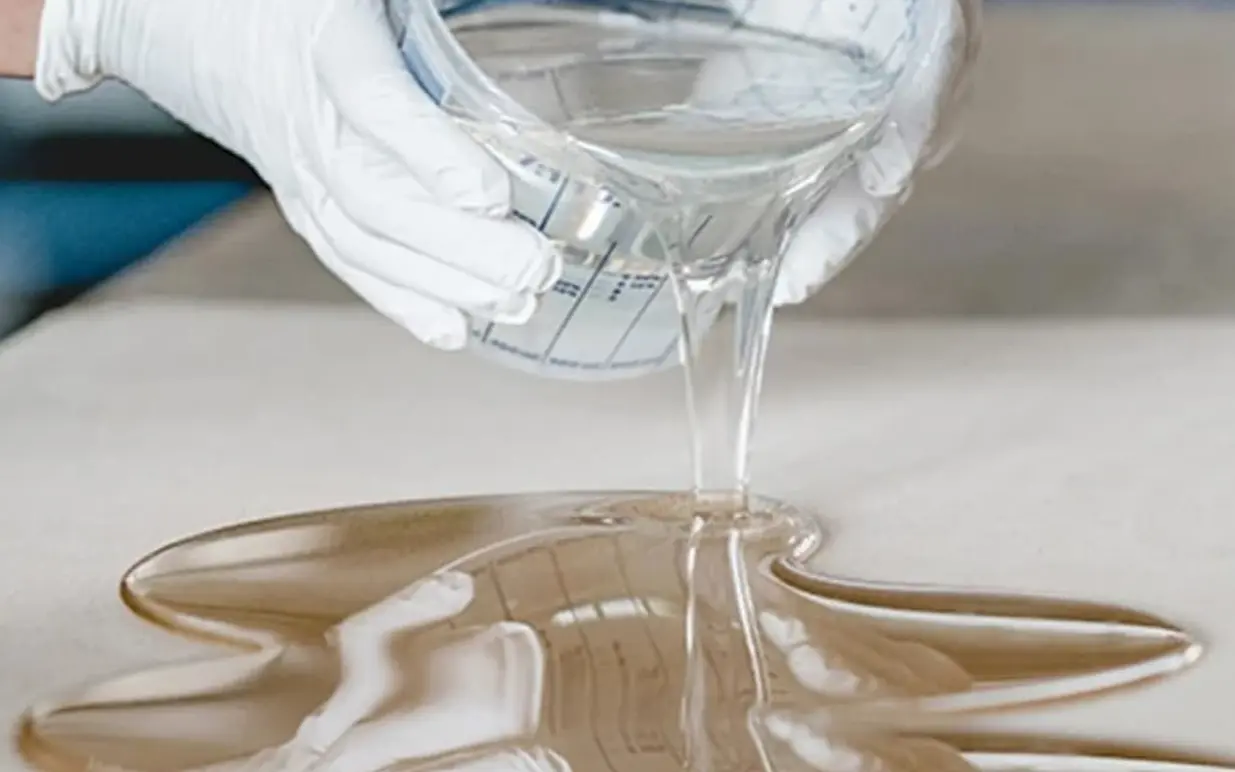

A significant application of epoxy resin is in the production of Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastics (GFRP). In this process, epoxy resin acts as a binding agent that holds together the glass fibers, creating a strong and lightweight composite material. GFRP composites made with epoxy resin are widely used in various industries such as marine, automotive, and construction due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and durability.
Types of Epoxy Resin
- Thermosetting epoxy resin: The most common type, when combined with a curing agent, forms a strong and permanent network of bonds that cannot be melted.
- Thermoplastic epoxy resin: This type of epoxy can be remelted when heated.
- Water-based epoxy resin: An environmentally friendly epoxy that is easy to use and less toxic.
Applications of Epoxy Resin
- Industry: Production of composite materials, coatings, adhesives, sealants, and electrical insulation materials.
- Construction: Waterproofing, epoxy flooring, reinforcing materials.
- Electronics: Manufacturing printed circuit boards, electronic components.
- Art: Creating handmade crafts, jewelry.
Advantages of Epoxy Resin
- High strength: Can withstand force, high temperature, and chemicals.
- Water resistance: Protects surfaces from moisture.
- Electrical insulation: Used in electronic devices.
- Excellent adhesion: Bonds strongly to various materials.
- Diverse colors and styles: Easily create aesthetically pleasing products.
Disadvantages of Epoxy Resin
- Curing time: Depending on the type of epoxy and environmental conditions, curing time can be quite long.
- Toxicity: Some types of epoxy can cause skin irritation and respiratory problems if not properly protected.
- Cost: Epoxy resin is often more expensive than other materials.
Epoxy Resin Manufacturing Process
- Epoxy synthesis: Creating epoxy molecules through chemical reactions.
- Mixing: Mixing epoxy with a curing agent in a specific ratio.
- Molding: Pouring the epoxy mixture into a mold and allowing it to cure.
- Processing: Cutting, grinding, and polishing the product after curing.
Precautions when using Epoxy Resin
- Personal protective equipment: Use gloves, masks, and safety glasses when working with epoxy.
- Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Mixing ratio: Adhere to the recommended mixing ratio between epoxy and curing agent provided by the manufacturer.
- Pot life: The epoxy mixture can only be used for a certain period of time after mixing.
Outstanding Applications of Epoxy Resin
Epoxy resin in construction:
- Waterproofing: Epoxy resin is used to create effective waterproofing coatings for surfaces such as walls, floors, roofs, and swimming pools.
- Epoxy flooring: Epoxy flooring is one of the most popular applications of epoxy resin.
- Reinforcing materials: Epoxy resin is used to reinforce concrete, steel, and wood structures that are damaged or cracked.
- Other applications: Used as an adhesive for tiles and natural stone, creating protective coatings for concrete surfaces, and manufacturing interior decoration products such as tables, chairs, and cabinets.
Epoxy resin in industry:
- Composite materials: Epoxy resin is a main component in the production of composite materials.
- Coatings: Epoxy coatings offer excellent corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and chemical resistance, and are used to protect metal, concrete, and wood surfaces.
- Adhesives: Epoxy adhesives have very high bonding strength, can withstand pulling forces and high temperatures, and are used to bond various materials such as metals, wood, plastics, and ceramics.
- Other applications: Manufacturing printed circuit boards, creating molds, and producing insulating products.



No comments.
You can be the first one to leave a comment.